pearlscale angelfish
| Scientific name | Centropyge vrolikii |
|---|---|
| Descriptor | Bleeker |
| Year of description | 1853 |
| IUCN category (World) | LC |
| Family | Pomacanthidae |
| Genus | Centropyge |


Introduction
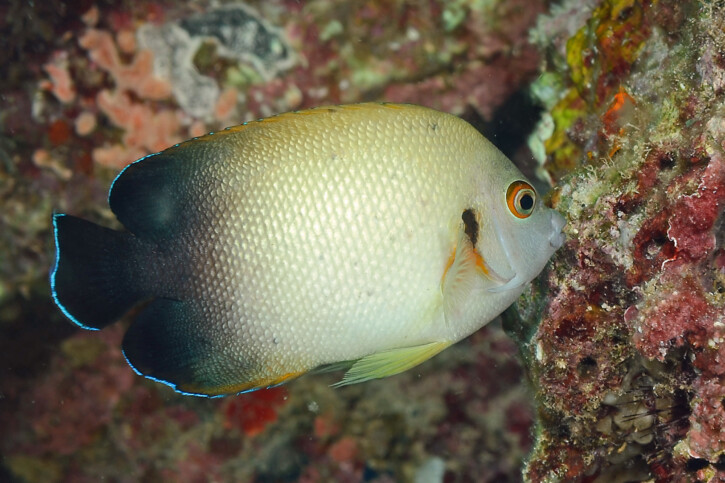
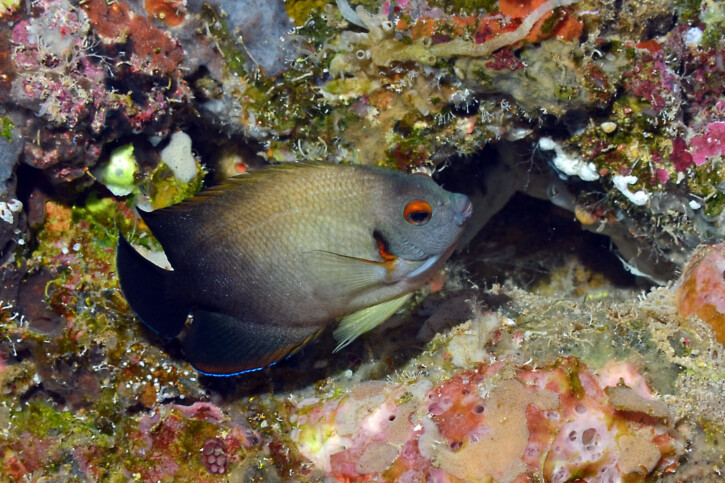
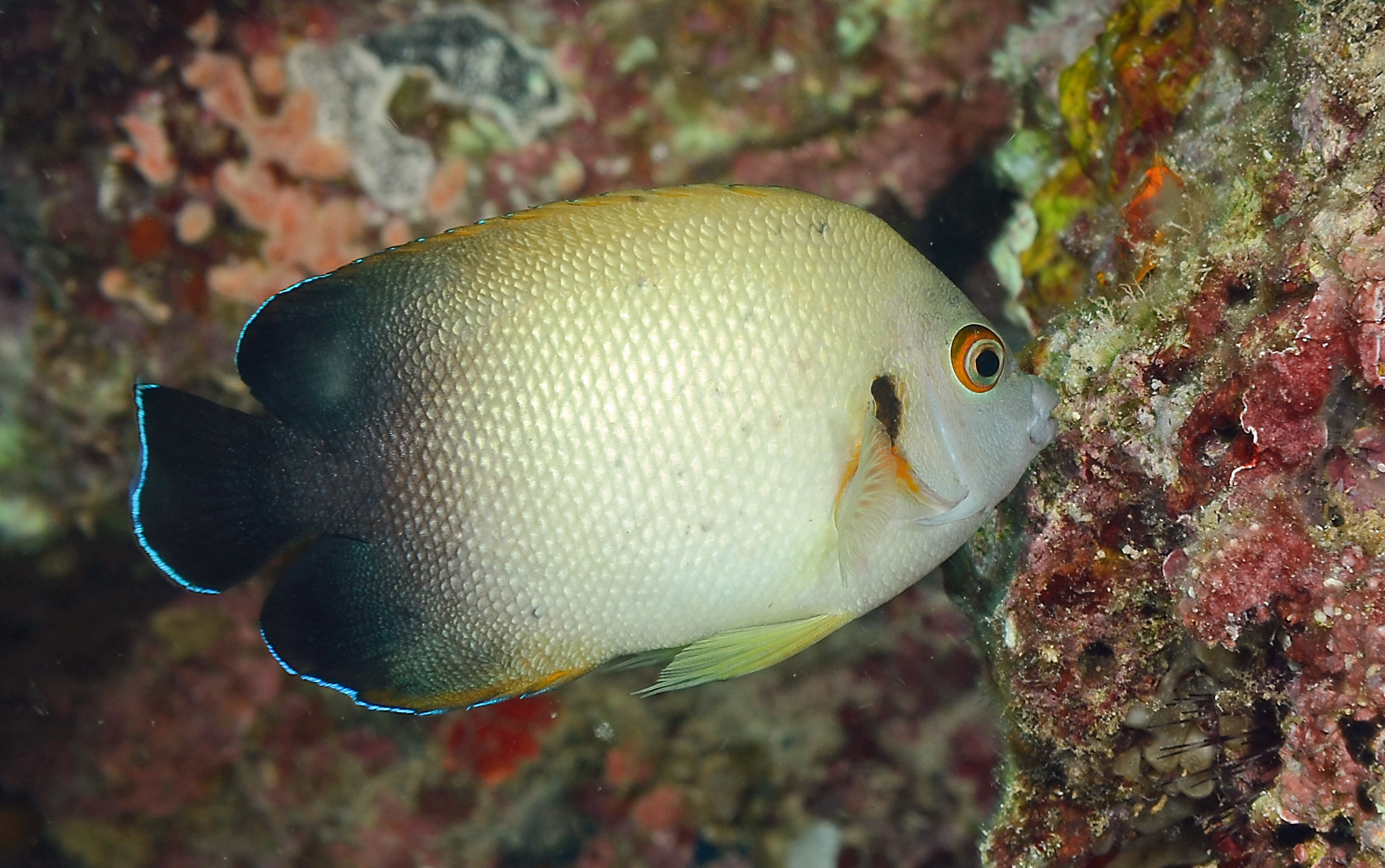
Centropyge vrolikii, commonly known as pearlscale angelfish, is a salt water fish.
This sheet is currently being prepared. The texts currently proposed come from our data model or are being drafted. To request priority for this content, you can write to us HERE.
Who is it?
Morphology
-
Average size10 cm
-
Maximum size12 cm
-
Longevity15 year
-
ShapeOvoid
-
Average size10 cm
-
Maximum size12 cm
-
Longevity15 year
-
ShapeOvoid
How to recognize This fish ?
The pearlscale angelfish measures around 10 cm. The dominant males can however reach 12 cm. This fish is multicolore with a predominantly jaune, vert, noir and gris body.
Sexual dimorphism
The adult male is bigger than the female.
Behaviour & Life cycle
-
dietomnivorous with alguivorous tendency
-
Sociabilityliving as a couple or alone
-
territorialNo
-
Way of livingdiurnal
The pearlscale angelfish is a fish living as a couple or alone naturally found at mid-depth and near the bottom. This species is omnivorous with alguivorous tendency .
Although the pearlscale angelfish is non-territorial, it is sometimes aggressive towards other species.
Reproduction
-
Reproductionovipare qui pond en eau libre
The pearlscale angelfish is a fish ovipare qui pond en eau libre. This fish protects its eggs from nearby predators.
Harmless species
This species does not represent any particular threats to humans when encountered in its natural environment.
Origin and distribution
What is its habitat?
Natural environment characteristics
-
Temperature26 - 29 °C
-
Depth1 - 25 m
Biotope presentation
The pearlscale angelfish is most often found at a depth between 1m and 25m. However, it is not impossible to find this species at other depths.
Species of the same biotope
Main recommendations for fishkeeping
Deontology
In order to preserve wildlife, if you acquire this animal, it must not be released into the wild. See also, the Fishipedia charter.
Fishipedia supports the practice of responsible and environmentally friendly aquarium keeping. We encourage maintenance if it is motivated by a desire to understand the biological functioning of living things and if it is done with respect for animal life.
We believe that aquaristics is an opening to the discovery of aquatic environments, especially freshwater, and that this knowledge is necessary to better protect and respect these environments. Logically, we refute the compulsive purchase of animals that would not find a sufficient and / or adapted place in the host aquarium.
Our recommendationsThese tips apply to adult species from breeding. With regards to water conditions, wild species or close relatives must be kept under the same conditions as in their area of origin.
-
Min volume300 liters
-
Population min1
-
Temperature26 - 29 °C
CharacteristicsThe characteristics below apply for adult species. They correspond to an average of cases, validated in maintenance condition.
-
Difficulty breedingThe farming difficulty is relative. It depends on experiments already carried out with similar species. First, it takes into consideration the robustness of the species, the ease of recreation of a favorable environment and the general behaviour with the other inhabitants of the aquarium.hard
-
Robustnesssensible
-
Behaviourslightly aggressive
-
Availabilityoccasional
General reminders
It is strongly advised to read the complete dedicated file and to get information on the feedbacks of maintenance of the envisaged animal, this to avoid any potential conflict whose end result is generally the death of the individual (or the other inhabitants). It is important not to overload your aquarium to limit pollution. This will make maintenance easier.
General reminder on maintenance datas
Le démarrage d'un aquarium est une partie primordiale pour l'équilibre et le bien-être des poissons. Lorsque l'on met en eau un aquarium, l'eau passe naturellement par un cycle biologique : le cycle de l'azote. Celui-ci dure environ trois semaines. Tous les 2 jours, nous vous conseillons de tester votre eau jusqu'à ce que le taux de nitrite soit à zéro pendant plusieurs jours d'affilée.
Pour accélérer ce cycle, vous pouvez utiliser un activateur de bactéries comme JBL Denitrol. Cette solution riche en bactéries vivantes et enzymes permet une mise en place rapide du cycle de l'azote. Les poissons peuvent alors être introduits plus rapidement.
Il est important de tester l'eau de son aquarium régulièrement pour maintenir un environnement sain pour les poissons et les autres habitants. Les tests d'eau permettent de mesurer les niveaux de différents paramètres tels que le pH, la dureté totale, ainsi que les taux de nitrates, de nitrites et d'ammoniaque.
Pour réaliser ces tests, vous pouvez utiliser des produits d'analyse spécialisés tels que JBL ProScan qui permet de réaliser un diagnostic de l'eau directement via un smartphone. Il existe également des coffrets de tests plus classiques de bandelettes, comme JBL PROAQUATEST.
En cas d’usage de l’eau du robinet, vous pouvez utiliser un conditionneur d’eau de type Biotopol de JBL pour éliminer les substances nocives comme le chlore, le cuivre, le plomb et le zinc. Les conditionneurs d'eau garantissent une meilleure santé aux poissons et une meilleure croissance des plantes.
Chlorine and chloramine are dangerous for the health of animals. Used to disinfect water, these agents are present in significant quantities in tap water. We recommend using an anti-chlorine agent every time you change the water. In addition to chlorine, treatments and medicines sold for aquarium use sometimes contain dangerous heavy metals in high doses.
Specific needs for the pearlscale angelfish
The pearlscale angelfish is a marine species which lives naturally at a temperature between 26 °C and 29 °C. For proper maintenance, the temperature should never exceed the 32°C for long periods. The pearlscale angelfish is sensitive to abrupt changes in parameters as well as to chemicals. Its acclimation in an aquarium must be done with special care to prevent it from developing diseases or weaknesses. Nitrate levels should remain below 25mg/L. To keep the water clean and unpolluted, plan on changing 20% to 30% of the water volume each month. In seawater, it is also possible to remove nitrates using one of the following methods: Jaubert, denitrator on sulfur, biopeletts, vodka method.
The pearlscale angelfish is a species whose maintenance is rather reserved for informed aquarists . It can only be successfully carried out by carrying out a minimum of documentation work. Special husbandry conditions can easily lead to the death of the species or other animals.
This species is generally available in specialized shops or from aquarium clubs. Specimens that have been bred for a long time are easier to breed, but special water parameters must be respected.
Formal incompatibilities
Cohabitation & Environment
In a community aquarium context, this species should be kept in a minimum volume of 300 liters.
Tips for feeding
The pearlscale angelfish is omnivorous with alguivorous tendency.
This species can eat dry food (flakes, pellets), fresh food and frozen food. To avoid deficiencies, it is recommended to vary the types of food.
You should not overfeed your residents to avoid polluting the water. For most species, it is better to feed a few small portions each day rather than one large meal.
Reproduction protocol
-
Spawning cleaningNo
-
egg-laying protectionNo
-
Fry protectionNo
Hybridization risks
In general, it is advised not to mix several species of the same genus or different varieties of the same species, to avoid the risks of hybridization.
These animals might interest you
These plants might interest you
Plants play a crucial role in aquariums, both for their ability to filter water by absorbing excess nutrients and for their aesthetic contribution. They provide fish with natural hiding places, can serve as breeding sites, and generally help maintain the overall balance and optimal conditions of the aquarium. The selection presented here includes species from the same regions as the species described on this page, although they do not necessarily come from its exact natural biotope.
To go further
Sources & Contributions
Participation & Validation
The Fishipedia team and specialist contributors are committed to providing high-quality content. However, although the information comes from scientific sources or testimonials from specialists, the cards may contain inaccuracies.

Adrien Falzon
Translation
Translation done with the valuable contribution of our translators, who make this information available to a wider audience. We sincerely thank them for their commitment.
Bibliographic references
Rapid transition in sexual behaviors during protogynous sex change in the haremic angelfish Centropyge vroliki (Pomacanthidae) - Yoichi Sakai - Chihiro Tsujimura - Yukari Nakata - Hisayo Tanabe - Go Maejima - Springer Nature - 2003.
Twisted sister species of pygmy angelfishes: discordance between taxonomy, coloration, and phylogenetics - Joseph D. DiBattista - Ellen Waldrop - Brian W. Bowen - Jennifer K. Schultz - Michelle R. Gaither - Richard L. Pyle - Luiz A. Rocha - Springer Nature - 2012.
Scientific partners
Tags
Species of the same family
Same genus
Species of the same biotope





































